Gaming is currently one of the most popular hobbies around the world. According to Statista, over 80% of all internet users play video games via any device, helping generate over $200 billion in revenue across all gaming platforms in 2022.
Games come in many shapes – with both 2D and 3D games being the most popular ones. When it comes to creating 3D games, one of the biggest conundrums a developer can face is the decades-old “high-poly vs low-poly models: which one should I use?”
In this article, we will explore what it means to be “high-poly” and “low-poly”, as well as the pros and cons of both creating and using them, giving you the knowledge to decide for yourself which one will be the best for your upcoming game.
Have a good read!
What are high-poly and low-poly after all?
High-poly and low-poly are self-explaining terms, but they can be elusive to outsiders. In 3D modeling and game development, they stand for “high polygon count” and “low polygon count” respectively, referring to the number of polygons a game’s models have. Generally speaking, higher polygon counts imply more detailed, life-like visuals, whereas lower numbers often result in minimalistic graphics – more on their differences later.
But that unearths another question: what the heck are polygons?
Well, they are the main components of polygonal modeling, one of the most widely used approaches to modeling. 3D artists can use polygons to represent (or, rather, approximate) the surface of real-world objects, creating a mesh. These polygons are flat shapes that are fully enclosed by lines (called “edges”), which join at the “vertices.” In most cases, triangles are the polygon of choice, though quadrilaterals have seen some use over the years.
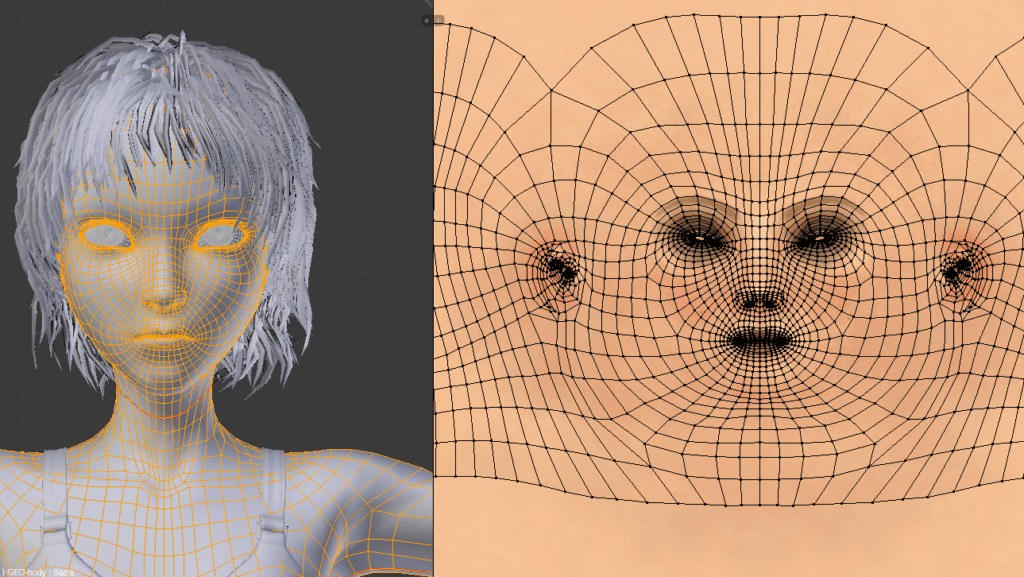
Without polygonal modeling, creating extensive 3D games would be almost impossible. We would still have ASCII and 2D games, but variety is the spice of life, isn’t it?
High-poly vs low-poly in game development
Even though there’s not a clear threshold at which a low-poly asset becomes a high-poly one and vice-versa, the threshold varies depending on the object being modeled. For example, using 1,000 polygons to represent a crate will likely deem it a high-poly asset whereas using the same 1,000 to represent a humanoid creature will definitely render it a low-poly asset.
In any case, let’s cover the differences between high-poly and low-poly models for games:
High polygon count
High-poly games are the favorite of the big gaming studios – think of Activision Blizzard, CD Projekt Red, Rockstar Games, Electronic Arts (EA), and Bethesda to name a few. And players love them, too: the 20 top-selling video games in the United States in 2022 were developed by AAA studios according to Statista.
That said, some indie developers have also hopped on the high-poly bandwagon, and the results were phenomenal. Stray, one of the most anticipated (and loved!) indie games to date, has realistic high-poly graphics following a cyberpunk aesthetic, which perfectly complements the game’s plot and universe. After all, who doesn’t love playing as a cute ginger cat?
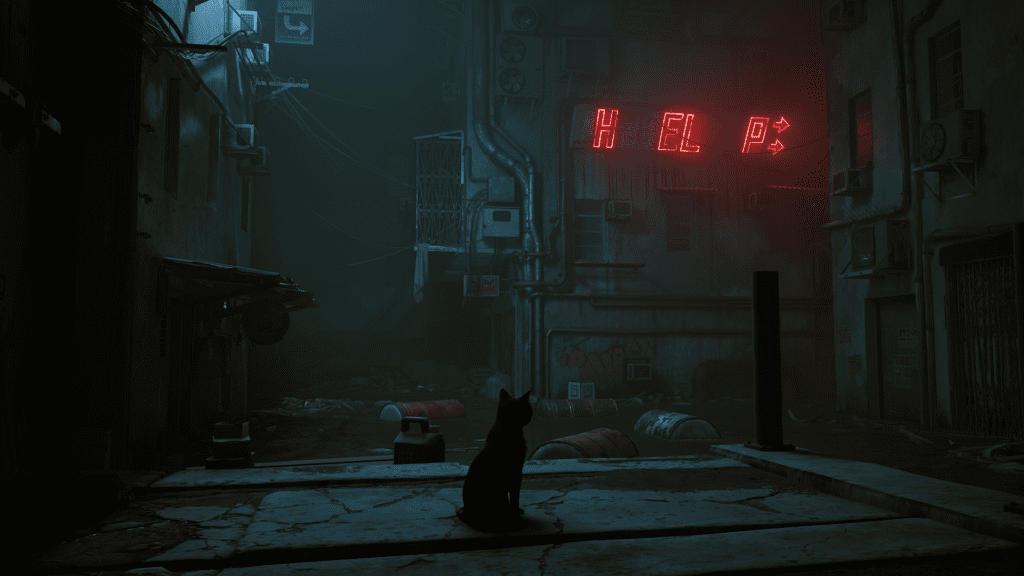
Nevertheless, it’s not all sunshine and flowers. Creating high-poly models for games has its own set of pros and cons, as we will see right below:
Advantages of creating high-poly assets
- They provide a visually rich experience: high-poly models provide a much greater level of detail than their low-poly counterparts, allowing for highly immersive and realistic characters, creatures, vegetation, buildings, and more;
- They grant more creative freedom: with higher polygon counts, game artists, and designers can create models that are extremely complex and intricate;
- Better lighting and shading: as high-poly models tend to be very detailed, lights and shadows can be calculated much more accurately, improving the visual quality of the game;
- Amazing animations: once the model has been rigged, developers can create awe-inspiring animations to use in trailers, promotional cinematics, and in-game cutscenes;
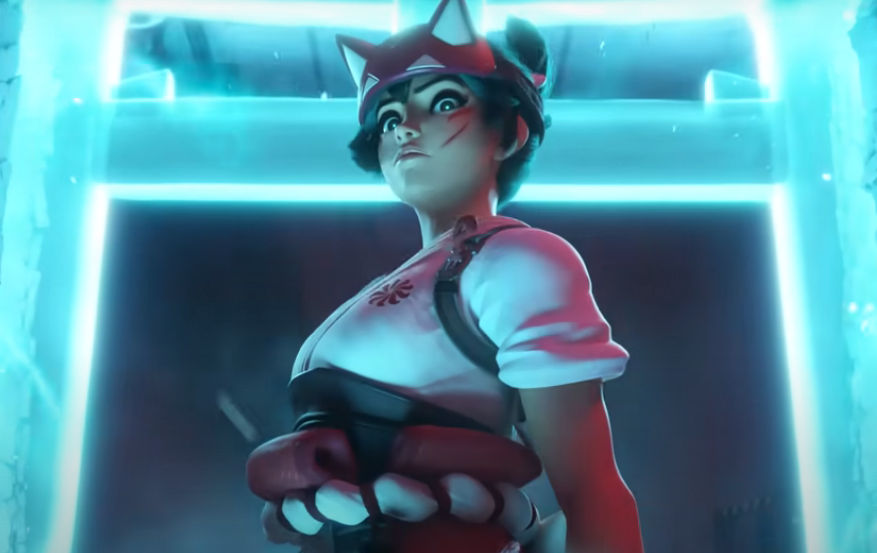

Disadvantages of creating high-poly assets
- They are hard to create: even with the best software out there, making high-poly game assets take a lot of time – from days to even weeks depending on the complexity of your object/creature. For this reason, production times of games using high-poly models are often longer than those using low-poly ones;
- Their file weights can get massive: the file size of these models is directly proportional to their polygon amount. Hence, high-poly assets often require more memory and storage, making the game larger and potentially causing slowdowns on less powerful computers;
- They are resource hogs: have you ever wondered why AAA games require increasingly powerful machines to run them? As the ability to process graphics grows with each generation of GPUs, so does the quality of the graphics on those big-ticket games – which, more often than not, have numerous assets with ridiculously high polygon counts.
Low polygon count
If, on one hand, we have high-poly games, we have low-poly ones on the other. These titles often have simpler, less detailed models, but that doesn’t mean they can’t make for fantastic visual experiences – sometimes, a distinctive and minimalist adventure with stylized graphics is all we need.
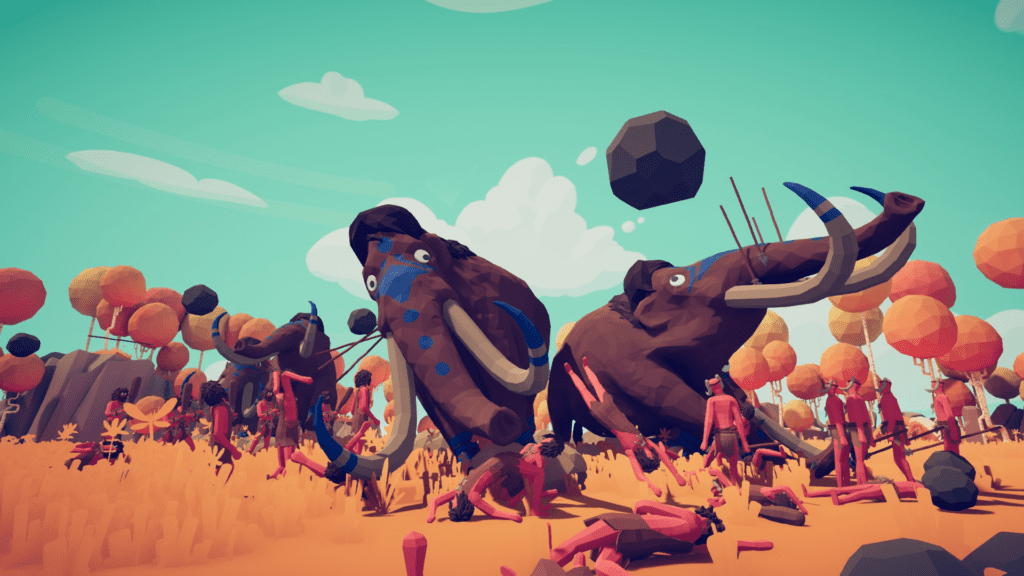

Their simplicity and ease of creation of game-ready low-poly assets often make them the choice of indie developers across the globe, offering unique experiences that appeal to a wide range of gamers. However, it’s important to keep in mind that there are pros and cons associated with this aesthetic:
Advantages of creating low-poly assets
- It is a charming art style: even though it’s not the best representation of the real world, many popular games are created in this budget-friendly art style. Totally Accurate Battle Simulator, better known as TABS, is one of the most successful titles following this art style, amassing over 95 thousand reviews on Steam alone;
- They are easy to create: unlike high-poly assets, models with lower polygon counts are much easier to create as you don’t need to obsess over the smallest details. For this reason, creating them is usually a short process, cutting down on development time. If you’re looking to buy some, then we have good news: their price tag is usually much lower than high-poly models;
- Lower file weights: as file size and polygon count are directly proportional to each other, creating low-poly models will result in smaller file sizes, which are much more convenient to store. This is why you will often find models with polygon counts on the lower end when dealing with AR and VR experiences, such as the Metaverse, as lower file weights make those experiences much faster to load and run;
- They are a great compromise between visuals and performance: low-poly assets are not as resource intensive as high-poly ones, ensuring people with slower computers can still play those games at high frame rates. This also makes low-poly models ideal for mobile games, as phones often have lower processing capabilities than computers;
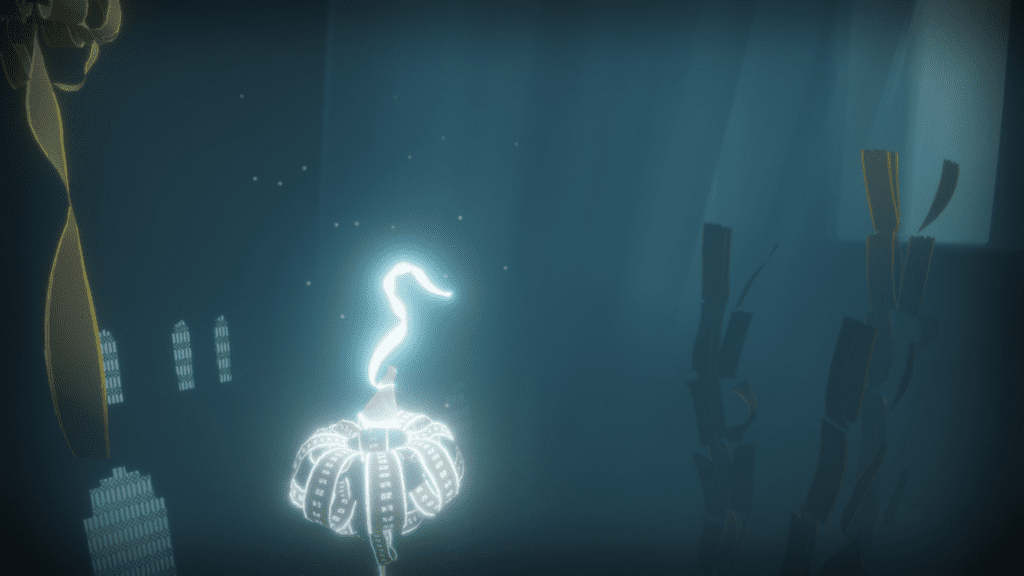

Disadvantages of creating low-poly assets
- They impair immersion and visual quality: low-poly models often skip on the tiniest details, which results in less realistic visuals, resulting in lower levels of immersion and realism. While this is not a deal-breaker for many players, it’s important to take this fact into consideration;
- They might feel “blockier”: as low-poly models often have flat faces and hard edges, they might feel too blocky when animated. Some say that’s part of their appeal, though;
- Effects might need to be added manually: if you’re looking to add reflection, shadows, refraction, and other effects into your model, you will likely have to do so manually;
- Limited creative freedom: unlike high-poly models, when you’re constrained to using fewer polygons to create something, your creative freedom can get very limited.
Choosing the Right Model: High-Poly vs. Low-Poly for 3D Design
In the realm of 3D modeling, the decision between high-poly and low-poly models is pivotal. Each type comes with its own set of advantages and considerations. High-poly 3D models are laden with detail, making them ideal for photorealistic rendering and intricate designs.
However, this complexity can demand substantial computational power, potentially affecting performance in real-time applications. On the other hand, low-poly models are streamlined, characterized by a lower polygon count. They are more performance-efficient, making them a go-to choice for interactive applications like games and 3D configurators.
The key is understanding when to utilize each approach: high-poly for that stunning visual richness, and low-poly for optimal performance. Whether you’re creating a high-poly 3D model for its accuracy or using low-poly for efficiency, your choice will largely depend on the specific demands of your project and the platforms it will run on.
So, which one should you use?
As you have read in this article, both high-poly and low-poly models have their own pros and cons. The former offers a higher level of detail, realism, and immersion, but actually creating them can take a long time, and they are huge resource hogs, often requiring powerful machines to fully experience them; the latter offers a lightweight and cost-effective solution for games with a lower level of detail, but low-poly models will still allow for incredible visual experiences.
So, how do you choose? Well, it really depends on the scope of your project, your budget, and what’s important to you.
Here’s our take. If you want to create a game that looks as realistic and immersive as possible, and you’re working with a large budget, you should go for high-poly models. If you want your game to run smoothly on a wider range of computer specs, if you’re working on a shoestring budget, or if you want to finish your game as soon as possible, you might want to opt for low-poly models.
Ultimately, the choice between high-poly and low-poly models comes down to your aspirations and resources as a game developer: it’s all about finding the happy medium that works best for your creation.
If you’re still unsure, well, you can leave this decision in the hands of an experienced game development studio. We are Main Leaf, a professional Brazilian-based game studio that has been on the market since 2010.
We offer a one-stop solution for game development in Unity and Unreal Engine, and we’d be pleased to bring the game of your dreams to life. Our roster of 70+ passionate professionals will take care of everything for you – from planning and design all the way to its release.
All you have to do is contact us by requesting a game quote on our main page. We’ll be waiting for you!

